What Is Dual In Logic . the dual of a boolean or of a boolean expression is obtained by applying 2 operations: the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. A complement depends on an. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary expression like x'y+xy'=1. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a.
from www.electronics-lab.com
According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary expression like x'y+xy'=1. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. A complement depends on an. the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. the dual of a boolean or of a boolean expression is obtained by applying 2 operations: if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and.
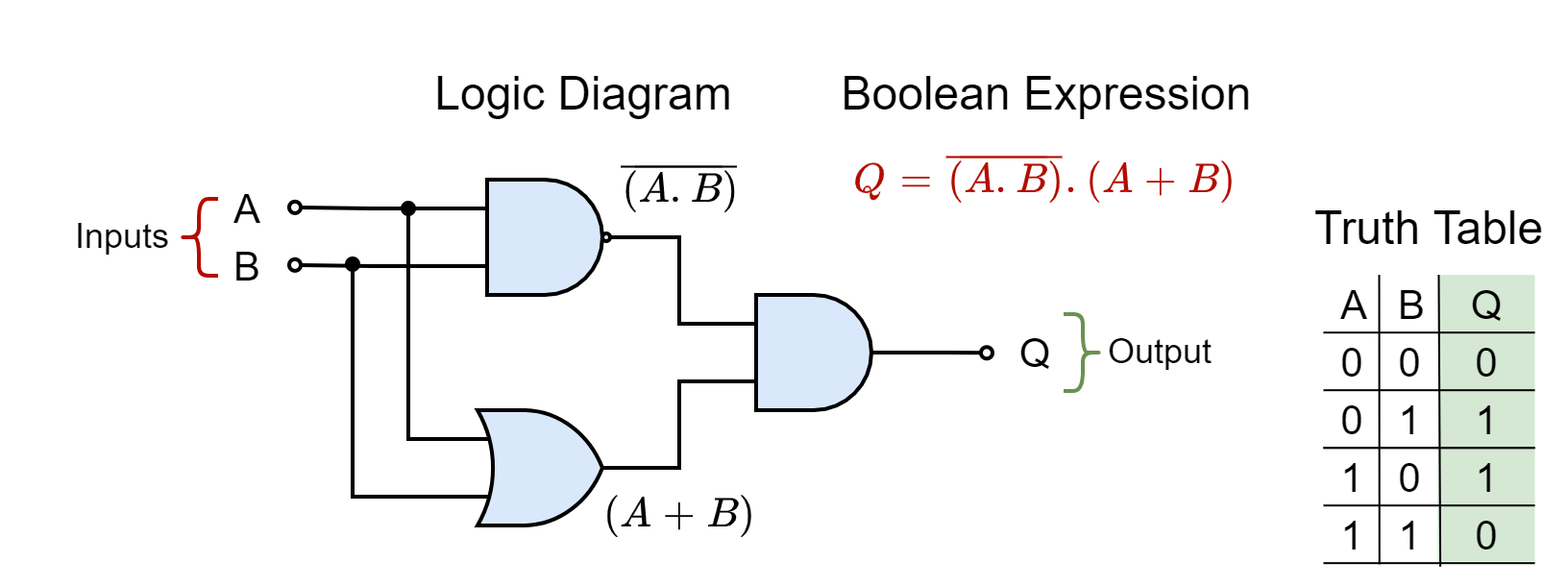
Combinational Logic Circuits
What Is Dual In Logic According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary expression like x'y+xy'=1. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. the dual of a boolean or of a boolean expression is obtained by applying 2 operations: A complement depends on an. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa.
From www.youtube.com
Proving and Simplifying Propositions using Logical Equivalence Laws What Is Dual In Logic the dual of a boolean or of a boolean expression is obtained by applying 2 operations: And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary expression like x'y+xy'=1. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. Web. What Is Dual In Logic.
From en.ppt-online.org
Binary Variables online presentation What Is Dual In Logic A complement depends on an. the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 1 from Logical Effort for CMOSBased Dual Mode Logic Gates What Is Dual In Logic the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. A complement depends on an. if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and.. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Logical Equivalences PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID What Is Dual In Logic And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. A complement depends on an. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. According to the duality principle, if we. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.electronics-lab.com
Combinational Logic Circuits What Is Dual In Logic According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. the dual of a boolean or of a boolean expression is obtained. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.youtube.com
Principle of Duality Boolean Algebra Fundamental of Digital What Is Dual In Logic According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary expression like x'y+xy'=1. the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. the duality. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.electroniclinic.com
Types of Logic Gate and its Applications Electronic Clinic What Is Dual In Logic According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary expression like x'y+xy'=1. A complement depends on an. And is the dual operation. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.hubberspot.com
How to use Logical Operators in Java ?. Learn Java by Examples What Is Dual In Logic if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. And is the dual operation. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.youtube.com
Principle of duality (solved problems) Dual network in network What Is Dual In Logic And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems. What Is Dual In Logic.
From mydiagram.online
[DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 4 To 1 Multiplexer What Is Dual In Logic A complement depends on an. the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and.. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.youtube.com
Truth tables for multiple logic gates YouTube What Is Dual In Logic the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. the dual of a boolean. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.youtube.com
Dual Form YouTube What Is Dual In Logic if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. the dual of a boolean or of a boolean expression is obtained by applying 2 operations: the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. the duality principle in mathematical. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.youtube.com
Discrete Math 1 Tutorial 22 Laws of Logic and Dual YouTube What Is Dual In Logic if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary expression like x'y+xy'=1. the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other,. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.youtube.com
DUALITY PRINCIPLE IN BOOLEAN ALGEBRA YouTube What Is Dual In Logic A complement depends on an. the dual of a boolean or of a boolean expression is obtained by applying 2 operations: if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. the two basic logical operations and and. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Which of the following logic expressions represent What Is Dual In Logic the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary expression like x'y+xy'=1. According to the duality principle, if we have postulates or if we have theorems of boolean algebra. if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.chegg.com
7.1 What is a logical dual? The two sentential What Is Dual In Logic there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary expression like x'y+xy'=1. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. According to. What Is Dual In Logic.
From www.nutsvolts.com
Small Logic Gates — The building blocks of versatile digital circuits What Is Dual In Logic if \(s*\) is obtained from \(s\) by making the substitutions \(\cup \to \cap\text{,}\) \(\cap \to \cup\text{,}\) \(\emptyset \to u\), and. the dual of a boolean or of a boolean expression is obtained by applying 2 operations: the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. According to the duality. What Is Dual In Logic.
From imathworks.com
[Math] Explanation of Solution substitution predicate logic Math What Is Dual In Logic the two basic logical operations and and or are called dual of each other, i.e. the duality principle in mathematical logic is a theorem on the acceptability of mutual substitution (in a. And is the dual operation of or and viceversa. A complement depends on an. there is no meaning to creating a dual from an arbitrary. What Is Dual In Logic.